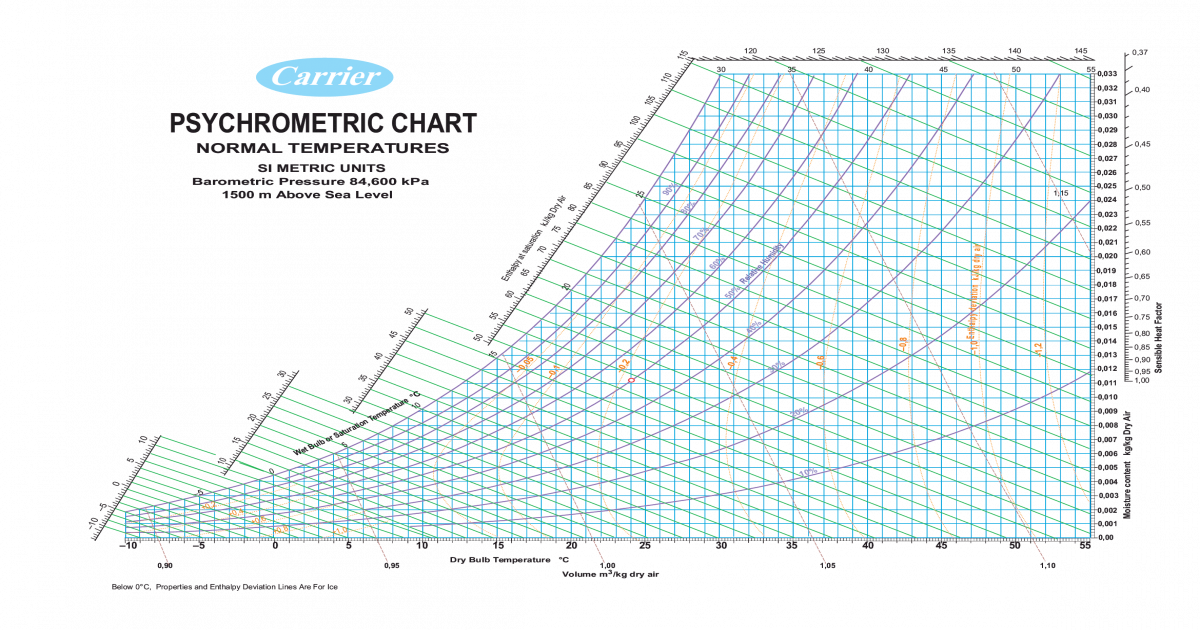
How to Use a Psychrometric Chart. Read or Download openinnew Opens in a new window. Carrier RTU with IGC Control Board – Sequence of Operations. Watch Video TRAINING. All Courses HVAC Design Software openinnew Curriculum Tracks Class Policies Seminars Our Instructors Schedule. A psychrometric process that involves the increase or decrease in the temperature of air without changing its humidity ratio Example: passing moist air over a. Use the psychrometric chart to determine the specific humidity ω 18 gm-moisture/kg-air, the enthalpy h 78 kJ/kg-air, the wet-bulb temperature T wb 25.5°C, the dew-point temperature T dp 23°C, and the specific volume of the dry air v 0.89m 3 /kg. Indicate all the values determined on the chart.
- Carrier Psychrometric Chart
- Metric Psychrometric Chart Pdf
- Carrier Psychrometric Chart Pdf Conversion
- Large Printable Psychrometric Chart
- Carrier Psychrometric Chart Pdf
Chapter 10: Air - Water Vapor Mixtures
b) The Psychrometric Chart andAir-Conditioning Processes
We notice from the development in Sectiona)that the equations relating relativeand specific humidity, temperature (wet and dry bulb), pressure (air,vapor) and enthalpy are quite tedious and inconvenient. For thisreason a PsychrometricChartrelating all the relevantvariables was developed which is extremely useful for designing andevaluating air-conditioning and cooling tower systems.
At first appearence the psychrometric chart is quiteconfusing, however with some practice it becomes an extremely usefultool for rapidly evaluating air-conditioning processes. The mostpopular chart in common usage is that developed by ASHRAE(American Society of Heating, Refrigeration andAir-Conditioning Engineers), however we feel that the construction ofa simplified version of the chart based on approximations of thevarious equations can be a very useful tool for developing anunderstanding of it's usage. This approach was suggested by MagedEl-Shaarawiin his article 'On thePsychrometric Chart' published in the ASHRAE Transactions (Paper#3736, Vol 100, Part 1, 1994) and inspired us to produce thefollowing simplified psychrometric chart:
Carrier Psychrometric Chart
The basic information used to construct the chart isthe water vapor saturation data (Tsat, Pg) which is obtained fromsteam tables over the range from Tsat = 0.01°C through 50°C. Thespecific humidity ω is then evaluated using the relative humidity φas a parameter to produce the various relative humidity curves (bluelines) as follows:
whereP is the standard atmospheric pressure 101.325 [kPa].
The saturation curve (100% relative humidity) alsoknown as the dew point curve is drawn as a redline. Notice that on the saturation curve the wet anddry bulb temperatures have the same values.
The major simplifying assumption in the constructionof the chart is that the enthalpy of the mixture is assumed to beconstant throughout the adiabatic saturation process (described inSectiona). This implies that the evaporatingliquid added does not significantly affect the enthalpy of theair-vapor mixture, leading to the constant slope wet bulb temperature/ enthalpy (red)lines defined by:
Notethat on the ω = 0 axis (dry air) h = T [°C]
Finally, the specific volume of the air-vapor mixture(greenlines)is determined from the ideal gas relation as
wherethe gas constant Rair=0.287 [kJ/kg.K]
It is normal practice to separate out the overlappingenthalpy / wet bulb temperature lines allowing them to be separatelyevaluated. Thus we introduce an oblique enthalpy axis and enthalpy(black) lines as follows:
The four equations highlighted above were programmedin MATLAB and used to plot the simplified psychrometric charts shownabove. Refer to the link:
MATLABprogram for plotting a Simplified Psychrometric Chart
An excellent NebGuide (University of Nebraska-LincolnExtension Publication) describing Howto use a Simplified Psychrometric Charthasbeen provided by David Shelton and Gerald Bodman. Another usefulguide provided by Mark Cartwright of the North Carolina ContractorTesting Institute (NCCTI) is the YouTube video: PsychrometricChart Simplified. Both guides reduce theconfusion by separately explaining 4 of the 6 sets of curves whichmake up a psychrometric chart. Definitely review both guides beforecontinuing.
Solved Problem 10.1 -Assumethat the outside air temperature is 32°C with a relative humidity φ= 60%. Use the psychrometric chart to determine the specific humidityω [18 gm-moisture/kg-air],the enthalpy h [78kJ/kg-air], the wet-bulb temperature Twb[25.5°C],the dew-point temperature Tdp[23°C],and the specific volume of the dry air v [0.89m3/kg].Indicate all the values determined on the chart.
Solved Problem 10.2:Assumethat the outside air temperature is 8°C. If the air in a room is at25°C with a relative humidity φ = 40%, use the psychrometric chartto determine if the windows of that room which are in contact withthe outside will become foggy.
Theair in contact with the windows will become colder until the dewpoint is reached. Notice that under the conditions of 25°C and 40%relative humidity the dew point temperature is slightly higher than10°C, At that point the water vapor condenses as the temperatureapproaches 8°C along the saturation line, and the windows willbecome foggy.
______________________________________________________________________________________
One of the major applications of the PsychrometricChart is in air conditioning, and we find that most humans feelcomfortable when the temperature is between 22°C and 27°C, and therelative humidity φ between 40% and 60%. This defines the 'comfortzone' which is portrayed on the Psychrometric Chart as shownbelow. Thus with the aid of the chart we either heat or cool, addmoisture or dehumidify as required in order to bring the air into thecomfort zone.

Metric Psychrometric Chart Pdf
Solved Problem 10.3:Outsideair at 35°C and 60% relative humidity is to be conditioned bycooling and heating so as to bring the air to within the 'comfortzone'. Using the Psychrometric Chart neatly plot the requiredair conditioning process and estimate (a) the amount of moistureremoved [11.5g-H20/kg-dry-air],(b) the heat removed [(1)-(2),qcool= 48kJ/kg-dry-air],and (c) the amount of heat added [(2)-(3),qheat= 10kJ/kg-dry-air].
Solved Problem 10.4:: Hotdry air at 40°C and 10% relative humidity passes through anevaporative cooler. Water is added as the air passes through a seriesof wicks and the mixture exits at 27°C. Using the psychrometricchart determine (a) the outlet relative humidity [45%],(b) the amount of water added [5.4g-H20/kg-dry-air],and (c) the lowest temperature that could be realized [18.5°C].
Carrier Psychrometric Chart Pdf Conversion
This type of cooler is extremely popular in hot, dryclimates, and is popularly known as a SwampCooler. An interesting application ofusing a swamp cooler to cool drinking water in extremely hotenvironments is described in the posting of Rich Oppel in the At Warblog of the New York Times: 'DrinkingFrom Socks'.
An interesting and informative description onPsychrometricChart Usefor livestock and greenhouseapplications has been presented in a PennState Extension website byEileen E. Fabian. Other websites that we found interesting is that ofWikipediaon Psychrometrics.
Large Printable Psychrometric Chart
______________________________________________________________________________________
Carrier Psychrometric Chart Pdf
Engineering Thermodynamics by IsraelUrieli is licensed under a CreativeCommons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United StatesLicense
